
News


Photosynthetically Utilized Radiation
This is the sum of light energy (expressed in megajoules) absorbed by phytoplankton in the entire water column below a surface area of 1 m2 during 24 h. Light energy is absorbed by the photosynthetic and photoprotecting pigments contained in phytoplankton cells suspended in the water. Part of this energy is converted into chemical energy during the photosynthesis of organic matter in these cells. Some of the remainder of this energy is converted into heat, which is released to the surroundings, while the rest radiates from the cell as light during luminescence (mainly the luminescence of chlorophyll a).
The PUR energy is defined by (Woźniak, 2008): $$PUR(z,t)= \int_{400nm}^{700nm}E_{0} (\lambda,z,t) a_{pl} (\lambda,z,t) d\lambda$$ where $$E_0 (\lambda, z, t)$$– spectrum of scalar irradiation at depth z $$a_{pl} (\lambda, z, t)$$– spectrum of the coefficient of light absorption by photosynthetic pigments in phytoplankton at depth z $$\lambda$$ - light wavelength [nm] $$z$$ –depth [m] $$t$$ - time [s] The 24 h PUR energy dose is obtained by integrating the PUR energy over depth (from the surface to 1.5 times the depth of the euphotic layer) and over time (24 hours).
Methodology
The PUR energy is determined using the DESAMBEM model (Woźniak et al., 2008). The input data for this model are the PAR radiation dose at the water surface and the concentration of chlorophyll a at the sea surface Ca(0).
The DESAMBEM model can be used to determine light fields in the water, from which the irradiance at particular depths can be calculated. One can also calculate vertical concentration profiles of photosynthetic pigments in phytoplankton (Majchrowski et al., 2007) and spectral coefficients of light absorption by photosynthetic pigments in phytoplankton at the same depths (Ficek et al. 2004). With these magnitudes to hand, one can calculate the 24 h dose of PUR energy.
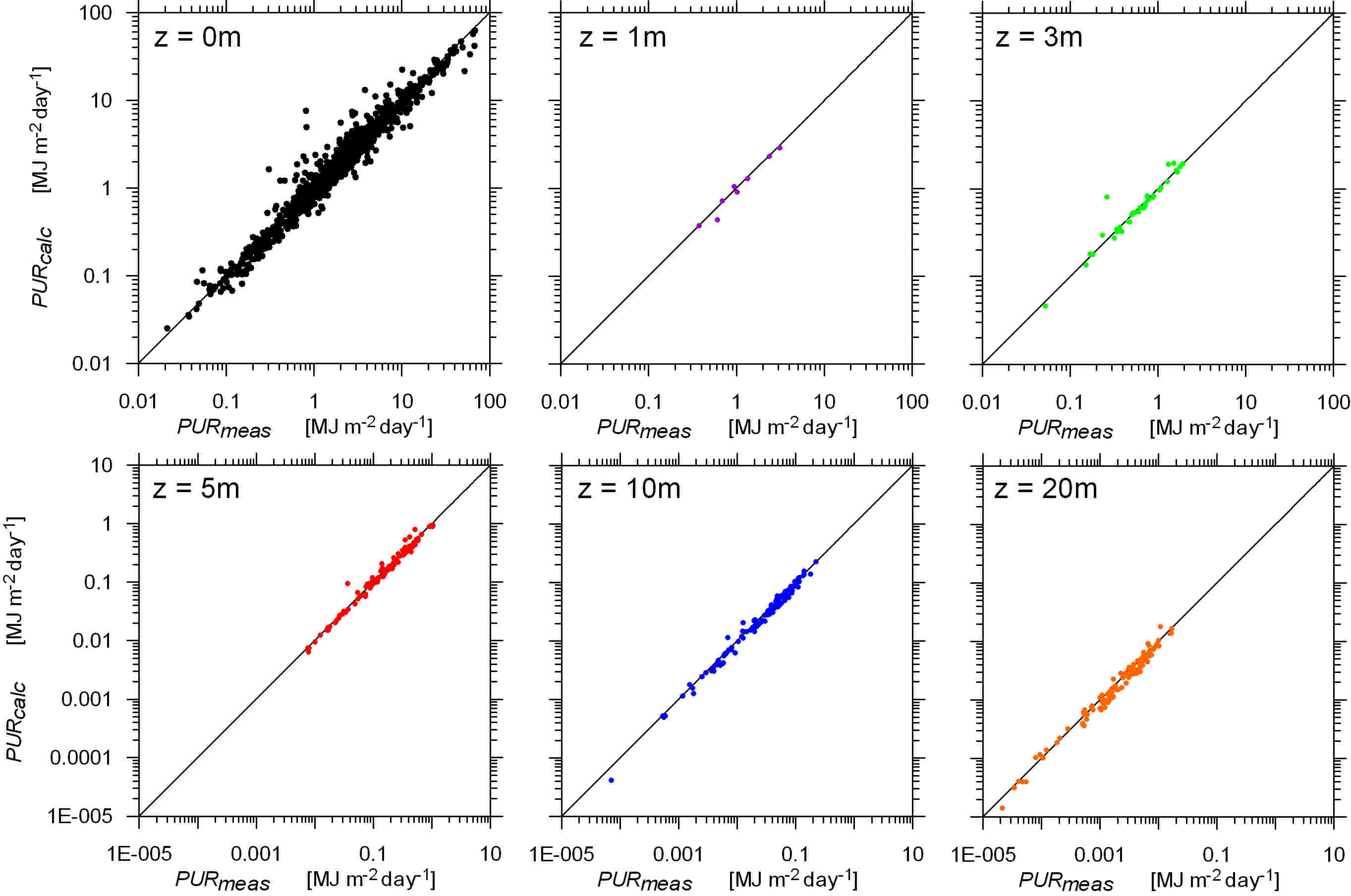 Fig.1 Comparison of empirical PURmeas and modelled PURcalc fluxes of PUR energy at different depths z in the euphotic layer of the Baltic Sea. The PURmeas fluxes were measured during research cruises in 2010-2014, while the PURcalc fluxes were calculated using the DESAMBEM algorithm. The input data included the surface concentration of chlorophyll a measured from on board ship.
Fig.1 Comparison of empirical PURmeas and modelled PURcalc fluxes of PUR energy at different depths z in the euphotic layer of the Baltic Sea. The PURmeas fluxes were measured during research cruises in 2010-2014, while the PURcalc fluxes were calculated using the DESAMBEM algorithm. The input data included the surface concentration of chlorophyll a measured from on board ship.Validation
The PUR energy was validated for the surface and selected depths in the Baltic. 1122 sets of surface measurement data were used to determine the PUR energy flux; they included measurements of the spectral coefficient of light absorption by phytoplankton aph and the PAR energy at the surface and at the depths for which the PUR energy was calculated. 132 sets of data relating to the depth profiles measured in 2010-2014 during research cruises, mainly in the southern Baltic, were also used. The standard error factor x (see the table below) characterizing the method for calculating the PUR flux, i.e. the flux of energy absorbed by algae, is relatively small and varies from 1.295 at the surface to 1.153 at 10 m depth. One can assume that the standard error factor x for the PUR flux in the entire water column does not exceed 1.295; in other words, the statistical error ranges from σ- = -22.8% to σ+ =29.5%.
Table 1. The systematic and statistical errors of PUR fluxes estimated at selected depths z in the Baltic Sea in arithmetic and logarithmic statistics when the input datum for the DESAMBEM algorithm was the chlorophyll a concentration at the surface measured from on board ship. N denotes the number of values estimated at a given depth.

|
Powstańców Warszawy 55 81-712 Sopot, Poland |
|
Write to us: |