
News


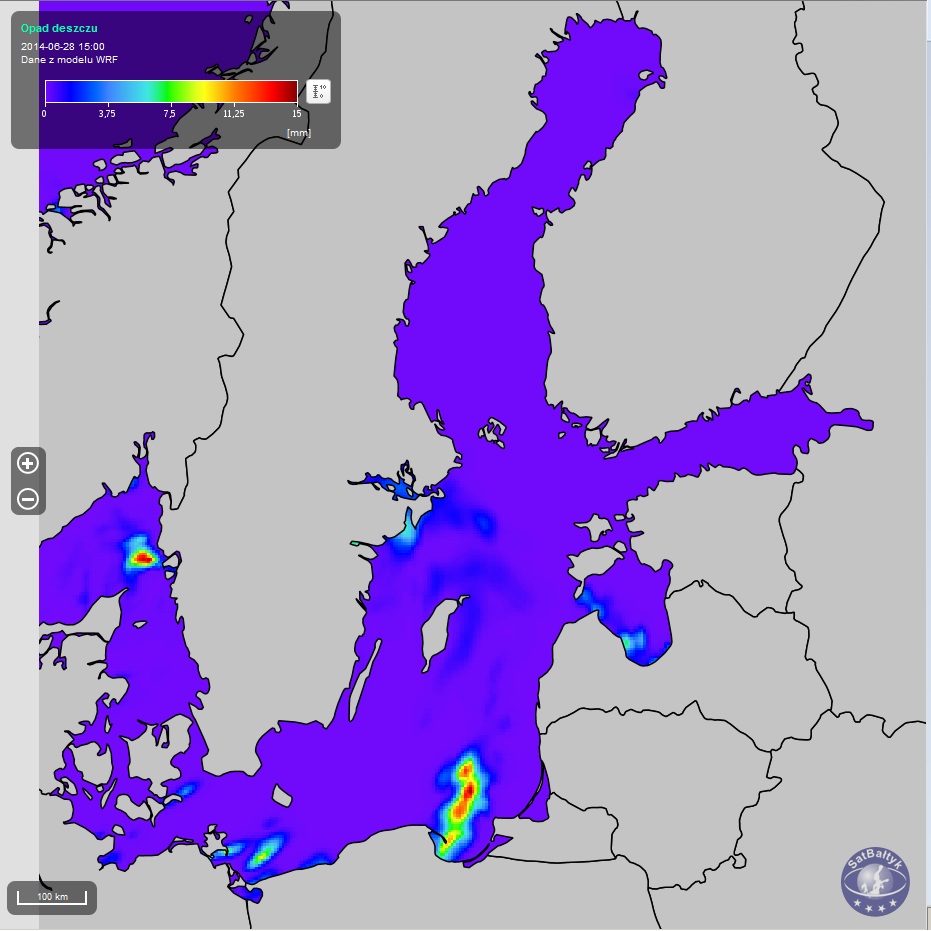
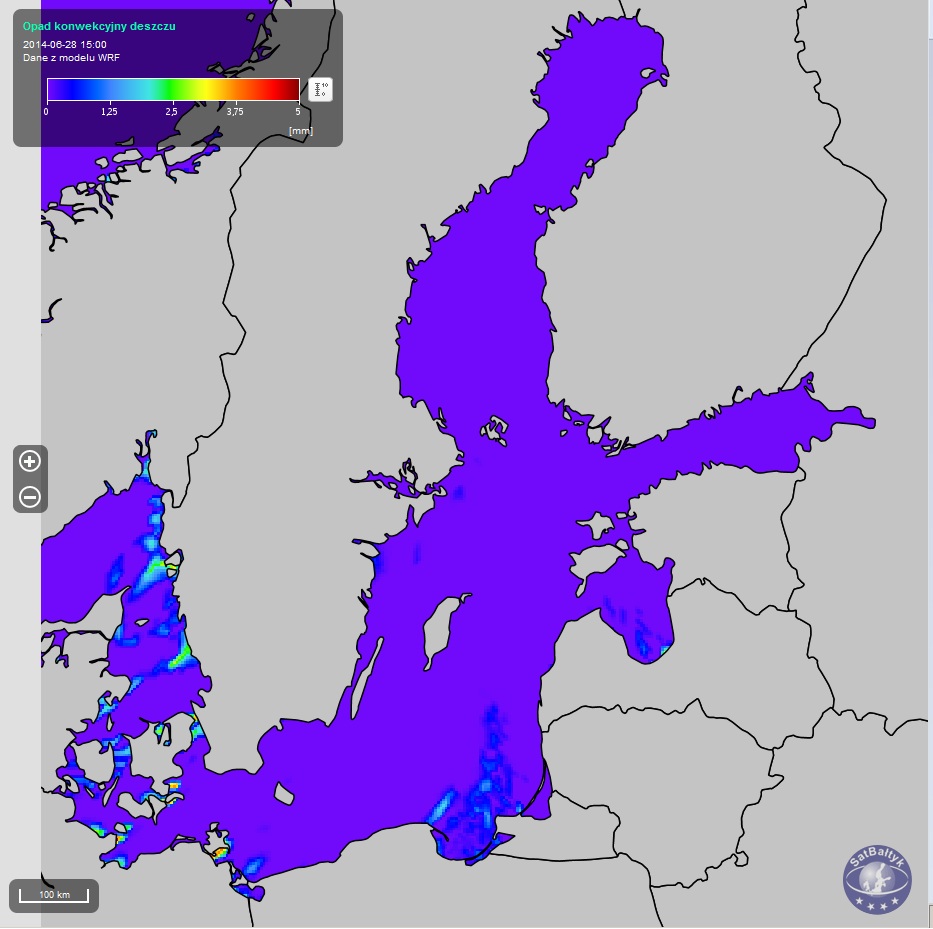
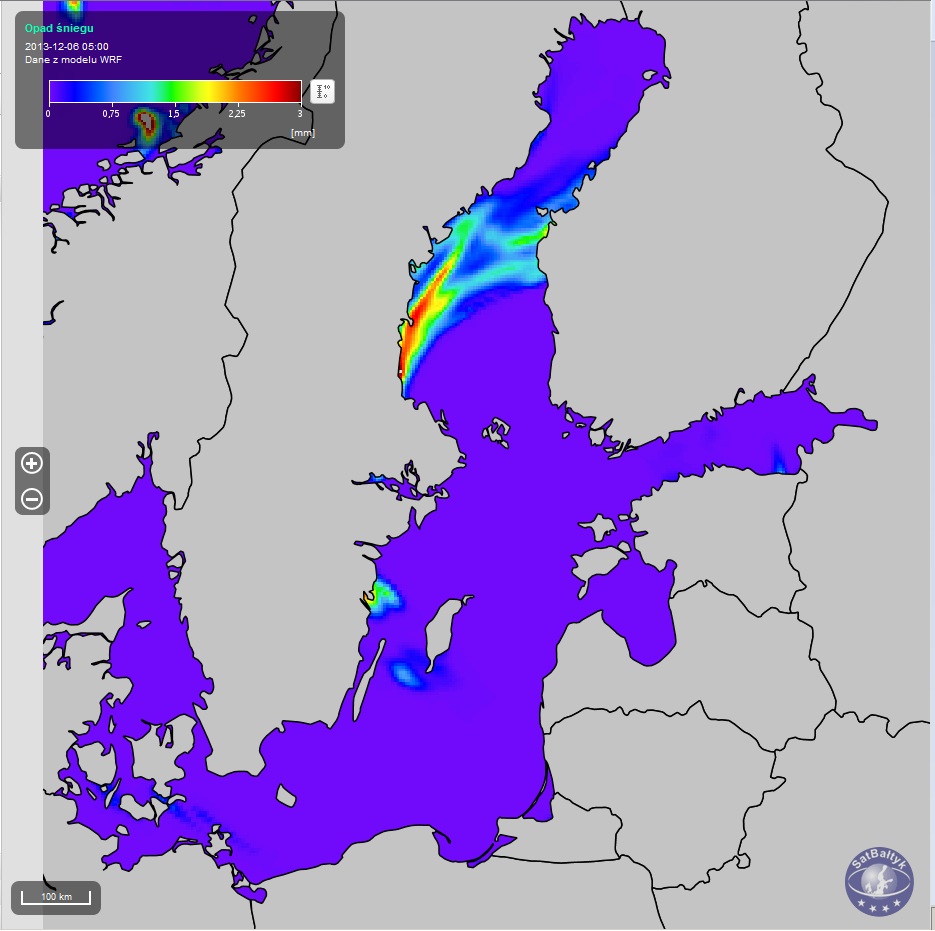 Maps of precipitation (rain, convectional rain and snow) over the Baltic, plotted using the WRF model.
Maps of precipitation (rain, convectional rain and snow) over the Baltic, plotted using the WRF model.The precipitation (rain, convectional rain, snow) obtained using a numerical weather map (representative of a 4×4 km area). In the SatBałtyk system, precipitation values express the height of a column of water/thickness of a layer of snow that falls onto a given area during one hour. Precipitation values (rain/snow) provide information on its intensity in liquid/solid form from all types of clouds, both stratiform and convectional. Since precipitation from convectional (e.g. thunderstorm) clouds is often exceptionally intense and torrential, it has been distinguished as a separate product – convectional rainfall. Precipitation is one of the basic variables in numerical weather models. The SatBałtyk system uses the WRF model (Weather Research and Forecasting), one of the most commonly used mesoscale weather models worldwide (suitable for analysing weather phenomena at a scale of several tens to several hundreds of kilometres, that is, a scale corresponding to the size of the Baltic Sea). In the SatBałtyk System, the WRF model covers the whole area of the Baltic Sea and uses the results of a global weather model as a source of information about adjacent areas. The details regarding the WRF model and its configuration in the SatBałtyk System can be found here.
The SatBałtyk System service provides distributions of precipitation intensity over the Baltic in metres [m], 24 times a day, in the form of maps with a resolution
of 4 km.
Methodology for determining precipitation intensity
The basic variable in the WRF model describing the intensity of precipitation is the mass (in kg) of water in the liquid/solid state falling to the ground in unit time. This mass is then converted to the height/thickness of a layer of water based on an assumed density. The intensity of precipitation is the result of an algorithm describing the so-called microphysics of clouds, that is, the physical processes involving phase changes of water in the atmosphere.
Validation (assessment of accuracy)
The accuracy of the precipitation maps is assessed on the basis of an analysis of the differences between measured and modelled values. The results of the model’s validation can be found here.
Rain precipitation (for registred users)
Convectional rain precipitation (for registred users)
Snow precipitation (for registred users)

|
Powstańców Warszawy 55 81-712 Sopot, Poland |
|
Write to us: |