
News


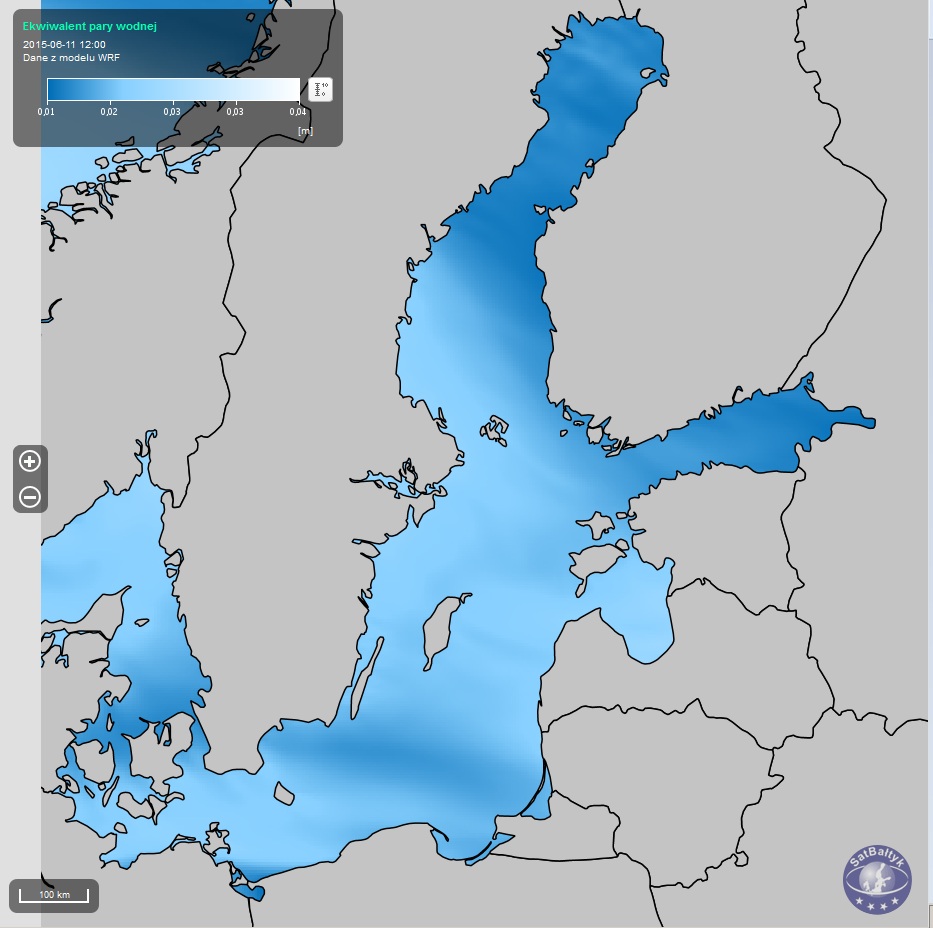 Maps of the water vapour equivalent and water equivalent of clouds over the Baltic plotted using the WRF model
Maps of the water vapour equivalent and water equivalent of clouds over the Baltic plotted using the WRF modelThe water vapour equivalent and water equivalent of clouds, obtained using a numerical weather model (representative of a 4×4 km area).
The water vapour /water equivalent is a measure of the total content of water vapour /water in the column of air over a particular spot. It is usually expressed in metres, as the thickness of the water layer that would be obtained if all the water vapour/water contained over a particular spot were collected in a vessel placed at that spot. These values provide important information about the properties of air masses and enable one to estimate, for example, the potential intensity of precipitation that under favourable circumstances could arise from these air masses. This is particularly important in, for example, thunderstorm situations, when the atmosphere is in a state of conditional stability.
The water vapour /water equivalent is determined on the basis of the absolute humidity of the various layers of the atmosphere, a basic variable in numerical weather models. The SatBałtyk system uses the WRF model (Weather Research and Forecasting), one of the most commonly used mesoscale weather models worldwide (suitable for analysing weather phenomena at a scale of several tens to several hundreds of kilometres, that is, a scale corresponding to the size of the Baltic Sea).
In the SatBałtyk System, the WRF model covers the whole area of the Baltic Sea and uses the results of a global weather model as a source of information about adjacent areas. The details regarding the WRF model and its configuration in the SatBałtyk System can be found here.
The SatBałtyk System service provides distributions of the water vapour equivalent and the water equivalent of clouds over the Baltic in metres [m], 24 times a day, in the form of maps with a resolution of 4 km.
Methodology for determining the water vapour equivalent and water equivalent of clouds
The fundamental variable in the WRF model, describing the water vapour content in the air, is the absolute humidity, defined as the mass (in kg) of water vapour per 1 kg of air. The water content in clouds is expressed in the same way. These variables, like all the other variables describing the state of the atmosphere, are determined on a three-dimensional grid covering the section of the atmosphere over the target area from the land/sea surface to the 50 hPa level, which lies at an altitude of approximately 20 km. The water vapour /water contents at particular grid nodes are obtained as the solution of the model’s basic equations. The water vapour/water equivalents are obtained by summing the masses of water vapour/water contained in the various layers.
Validation (assessment of accuracy)
The accuracy of the maps of water/water vapour equivalents is assessed on the basis of an analysis of the differences between measured and modelled values. The results of the model’s validation can be found here.
Water vapour equivalent (for registred users)
Water equivalent of clouds (for registred users)

|
Powstańców Warszawy 55 81-712 Sopot, Poland |
|
Write to us: |